Smart Configurator Specification
Requirements
| # | Title | User Story | Importance | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Optimizing global settings | Optimum settings for files location and Java virtual machine settings are computed by running hardware benchmark (disks) , detecting hardware types (RAM, OS), and using these values to retrieve optimum values from a database. | Must Have | S2 RQT 87 |
| 2 | Optimizing processing settings | For processing related settings (tile size, cache size, nb threads, etc.), optimum values are computed by running benchmarks for a combination of settings on a predefined graph. The user is able to define the values to be tested and the graph. | Must Have | S2 RQT 88 |
| 3 | Manual configuration | The optimizer presents the values of the set parameters to the user and offers the possibility to set the parameters manually. | Must Have | S2 RQT 89 |
| 4 | Launch mode | The optimiser can be launched during the installation. It is also be possible to re-run the optimizer after installation to update/reset the parameter values. | Must Have | S2 RQT 90 |
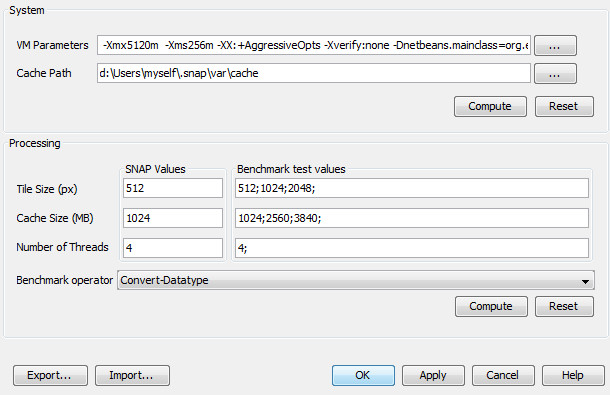
Find automatically the best parameters for SNAP, considering hardware and a processing chain. Currently, the GPF works by processing single tiles instead of entire images allowing processing of data larger than the available RAM by using tiled processing within their own threads. However, its tile cache memory and the Java VM’s heap space can be exhausted if it is not properly configured for large data volumes specifically for the user's computer system. Tile sizes and tile cache sizes are static values defined in a configuration file. Maximum heap space is a VM setting. Most users are unaware how to properly set and adjust these settings, this will be done by the Smart Configurator. The administrator starts the installer up to the smart configurator page [The administrator chooses to launch the smart configurator] [The administrator chooses NOT to launch the smart configurator] The installer proposes to launch the Toolbox The radiometry expert starts the Toolbox, then the Smart Configurator The Smart Configurator displays the parameters values The radiometry expert chooses the “land” processing graph The radiometry expert adds and remove values for possible cache size, tile size or number of threads The radiometry expert starts the bechmark The Smart Configurator computes all combinations for the "land" processing graph and displays the fastest parameters The radiometry expert changes some settings The radiometry expert clicks The smart configurator has two zones Three main actions are possible: For System settings For Processing settings Goals
Background and strategic fit
Assumptions
Use Cases
Use Case 1, installation
Use Case 2, from SNAP
User interaction and design
Not Doing